Hướng dẫn giải của Bedao Mini Contest 25 - Ước chia hết
Nộp một lời giải chính thức trước khi tự giải là một hành động có thể bị ban.
Subtask 1: ~N \leq 10^6~
For this subtask, we can check all numbers from ~1~ to ~N~ to see which ones are both divisors of ~N~ and divisible by at least two of the three numbers ~A, B, C~.
Complexity: ~O(N)~.
Subtask 2: ~N \leq 10^{12}~
We will try to reduce the complexity by finding all positive divisors of ~N~ within ~\sqrt{N}~. You can read more about it here.
Complexity: ~O(\sqrt{N})~.
Subtask 3: ~N \leq 10^{18}~ and ~A,B,C \geq 10^{6}~
Before diving into the analysis, we will make two small observations:
Observation 1: If a positive integer ~k~ is a divisor of the number ~n~ and ~k~ is divisible by ~x~, then ~n~ is also divisible by ~x~.
Observation 2: The positive integer ~n~ is divisible by two positive integers ~A~ and ~B~ if and only if ~n~ is divisible by the Least Common Multiple of ~A~ and ~B~.
To find the number of divisors divisible by ~2~ out of ~3~, we will apply inclusion-exclusion. Let ~f(X)~ be the number of divisors of ~N~ that are divisible by ~X~.
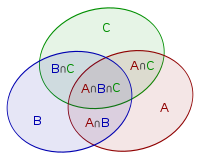
From the Venn diagram and Observation 2, it is easy to derive the formula ~f[LCM(A,B)] + f[LCM(B,C)] + f[LCM(C,A)] - 2 \times f[LCM(A,B,C)]~.
Finally, how to find ~f(X)~ with ~N \leq 10^{18}~? If there does not exist any integer ~k~ such that ~N = k\cdot X~, then ~f(X) = 0~. Conversely, we will have ~N = k\cdot a\cdot X~ where ~k~ is an integer and ~a~ is a divisor of ~N~. Thus, we only need to count the number of satisfying ~a = \frac{N}{kX}~, or in other words, find the number of divisors of ~\frac{N}{X}~.
Note that when finding ~LCM(A,B)~, we need to check if that number exceeds ~N~ to avoid overflow.
Complexity: ~O(\sqrt{\frac{N}{X}}) \sim O(\sqrt{10^{12}}) = O(10^6)~ with ~X \sim \min(A,B,C)~.
#include<iostream> #include<stdio.h> using namespace std; long long A,B,C,N; long long AB, BC, CA, ABC; long long res = 0; long long GCD(long long a,long long b) { long long r; while(b != 0) { r = a%b; a = b; b = r; } return a; } // LCM(a,b) = a*b/GCD(a,b) <= n // => b/GCD(a,b) <= n/a long long LCM(long long a,long long b) { if(a == -1 || b == -1) return -1; long long g = GCD(a,b); // Nếu LCM(a,b) > N thì bỏ qua if(b/g > N/a) return -1; return (a/g)*b; } long long solve(long long N,long long q) { if(q == -1) return 0; if(N%q != 0) return 0; long long n = N/q; long long res = 0; for(long long i = 1;i*i <= n;i++) if(n%i == 0) { if(i*i == n) res++; else res += 2; } return res; } int main() { cin >> N >> A >> B >> C; AB = LCM(A,B); BC = LCM(B,C); CA = LCM(C,A); ABC = LCM(LCM(A,B),C); res = solve(N,AB) + solve(N,BC) + solve(N,CA) - 2*solve(N,ABC); cout << res; }
Bình luận